Carleton University - School of Computer Science Honours Project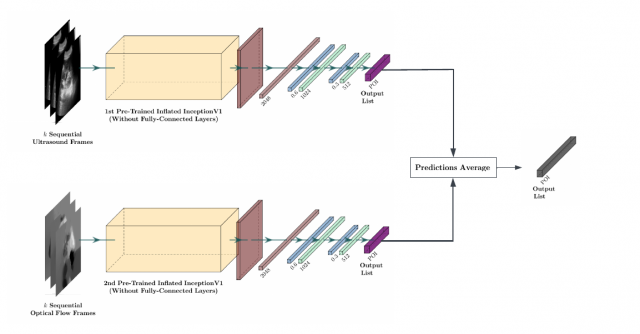
Winter 2022
Classifying points of interest in FAST ultrasound videos using deep neural networks

ABSTRACT
Focused Assessment with Sonography in Trauma (FAST) is an ultrasound procedure that assists in detecting free fluid in a patient's body as a possible indication of physical trauma. The FAST procedure examines four separate body regions: the Left Upper Quadrant, the Right Upper Quadrant, the Pericardium, and the Pelvic region. Within each region, there are Points of Interest (POIs) identified by medical experts as important locations on the body that require scanning as part of a comprehensive exam. This research explores methods for training and evaluating different Convolutional Neural Network architectures to classify which POIs have been scanned. As multiple POIs can appear close to one another in the same ultrasound frame, this task was formulated as a multi-label classification problem. First, a modified InceptionV3 model was trained and evaluated for POI predictions using single frames extracted from the ultrasound videos as input. Next, a modified Inflated 3D ConvNet (I3D) was used to predict the POIs using smaller videos extracted from the full ultrasound video as input for video classification. The best performing model was the modified InceptionV3 model that predicted POIs using single frames as input, having achieved a full-label accuracy of 88.5% with a micro F1-score of 0.65. One of the limitations in the performance is the small dataset size. More ultrasound videos or additional data augmentation techniques are required to further improve the models' performance. These results demonstrate a potential for using a POI classifier to provide objective feedback to ultrasound operators and can ultimately be used as a method for skill evaluation and as a real-time information system for the FAST assessment.